728x90
이번엔 Map을 mapping 해본다.
이런 테이블이 있다고 해보자.

import jakarta.persistence.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Entity
@Table(name = "book")
public class book {
@Id
private String id;
private String title;
private String content;
@ElementCollection
@CollectionTable(
name = "book_prop",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name="book_id")
)
@MapKeyColumn(name = "name")
@Column(name = "value")
private Map<String, String> props = new HashMap<>();
protected book(){}
public book(String id, String title, String content, Map<String, String> props) {
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
this.props = props;
}
//getter... setter...
}이렇게 @CollectionTable로 저장할 테이블을 지정을 해주고
Map에 들어간 데이터를 어떤 column에 넣어줄지 PK는 @MapKeyColumn에, 그냥 데이터는 @Column으로 지정을 해준다.
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManager;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityTransaction;
import jakarta.persistence.Persistence;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class book_main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("jpabegin");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction entityTransaction = entityManager.getTransaction();
Map<String, String> props1 = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, String> props2 = new HashMap<>();
props1.put("name1", "value1");
props1.put("name2", "value2");
book book1 = new book("1", "이름", "내용", props1);
book book2;
try{
entityTransaction.begin();
entityManager.persist(book1);
entityTransaction.commit();
}catch(NullPointerException exception){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
try{
book2 = entityManager.find(book.class, "1");
}catch(NullPointerException exception){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
System.out.println("book: " + book2);
System.out.println("props: " + book2.getProps());
}
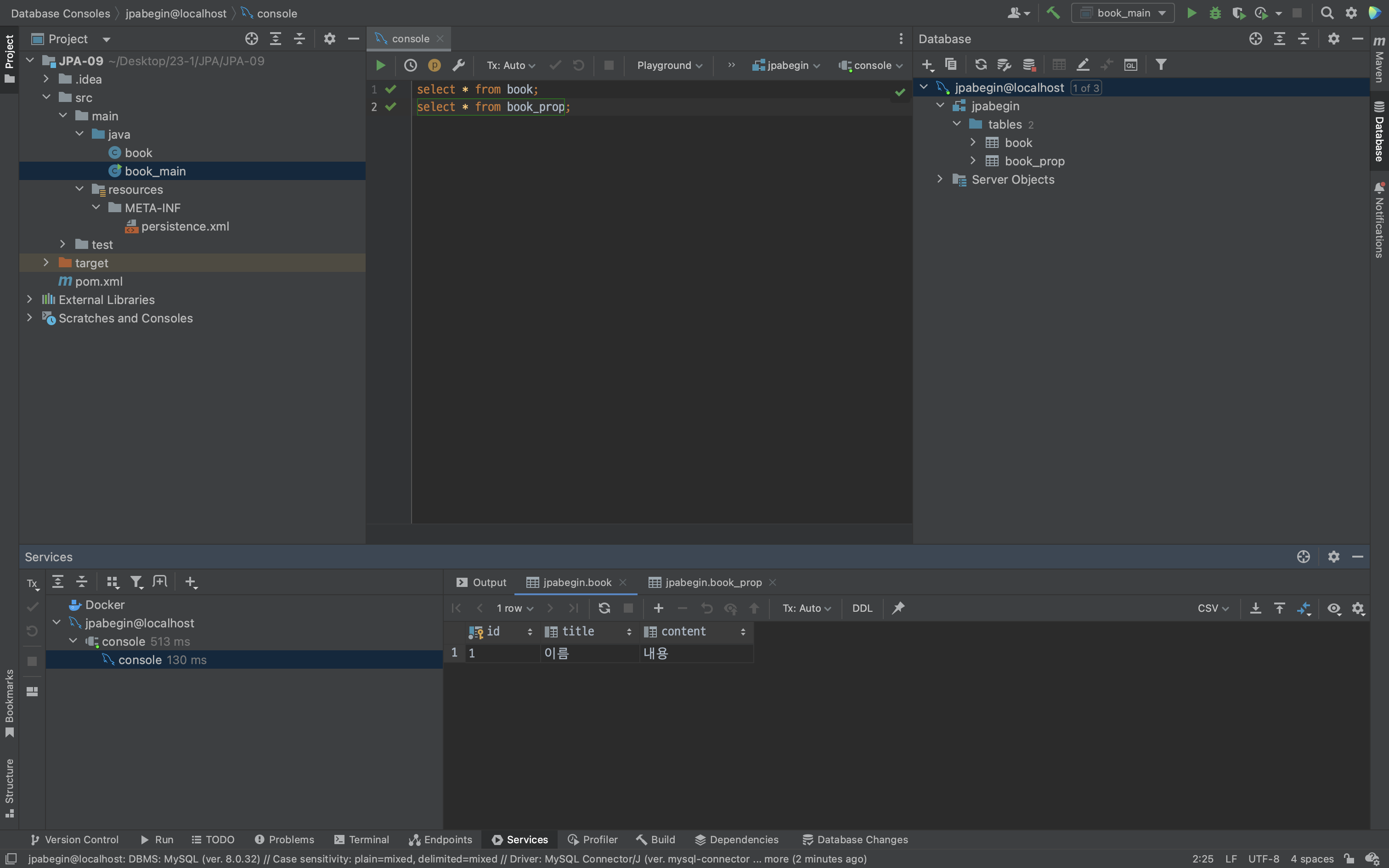
}이렇게 추가를 하고 조회를 하면

정상 작동하는 것을 볼 수 있다.

늘 그렇듯이 이번엔 Embeddable 타입이다.

이런 테이블이 있다고 하고, 여기서 PropValue를 Embeddable로 만들 생각이다.
우선 Embeddable 타입을 먼저 작성한다.
import jakarta.persistence.Access;
import jakarta.persistence.AccessType;
import jakarta.persistence.Embeddable;
@Embeddable
@Access(AccessType.FIELD)
public class PropValue {
private String value;
private boolean enabled;
public PropValue(String value, boolean enabled) {
this.value = value;
this.enabled = enabled;
}
protected PropValue () {}
//getter...setter...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PropValue{" +
"value='" + value + '\'' +
", enabled=" + enabled +
'}';
}
}이렇게 항상 작성하던 @Embeddable을 작성하고
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Entity
@Table(name = "book")
public class book2 {
@Id
private String id;
private String title;
private String content;
@ElementCollection
@CollectionTable(
name = "book_prop",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "book_id")
)
@MapKeyColumn(name = "name")
private Map<String, PropValue> props = new HashMap<>();
//getter...setter...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "book2{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", props=" + props +
'}';
}
}@MapKeyColumn을 이용해서 그랬던 것처럼 작성을 해준다.
여기에 Map의 타입에 <PK, @Embeddable>을 넣어서 작성해준다.
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManager;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityTransaction;
import jakarta.persistence.Persistence;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class book_main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("jpabegin");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction entityTransaction = entityManager.getTransaction();
Map<String, PropValue> Propvalues = new HashMap<>();
PropValue propValue1 = new PropValue("value1", true);
PropValue propValue2 = new PropValue("value2", true);
Propvalues.put("String1", propValue1);
Propvalues.put("String2", propValue2);
book2 book1 = new book2("id1", "title1", "content1", Propvalues);
book2 book2;
try{
entityTransaction.begin();
entityManager.persist(book1);
entityTransaction.commit();
}catch (NullPointerException exception){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
try{
book2 = entityManager.find(book2.class, "id1");
System.out.println(book2);
}catch(NullPointerException exception){
throw new NullPointerException();
}finally {
entityManager.close();
}
entityManagerFactory.close();
}
}
이렇게 동작하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
'백엔드 > JPA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JPA 10장 (영속 컨텍스트와 LifeCycle) (0) | 2023.03.22 |
|---|---|
| JPA 8장 (List collection mapping) (0) | 2023.03.18 |
| JPA 7장 (Set collection mapping) (0) | 2023.03.18 |
| JPA 6장 (@Embeddable) (0) | 2023.03.17 |
| JPA 5장 (Entity 식별자 생성 방식) (0) | 2023.03.16 |